Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes and some of these changes can lead to certain medical conditions. One such condition that affects men as they age is secondary hypogonadism. It is important to understand what secondary hypogonadism is and how it differs from primary hypogonadism. In this section, we will take a closer look at the definition of secondary hypogonadism and how it can impact a man's life.
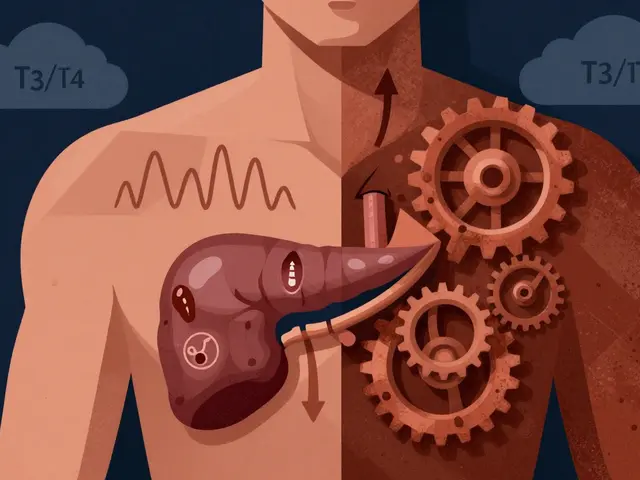
Secondary hypogonadism is a medical condition that occurs when the testicles do not produce enough testosterone, which is the primary male sex hormone. This is different from primary hypogonadism, where the problem lies within the testicles themselves. In secondary hypogonadism, the issue is with the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland, which are responsible for sending signals to the testicles to produce testosterone. As a result, men with secondary hypogonadism may experience a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, low libido, and erectile dysfunction.
Causes and Risk Factors of Secondary Hypogonadism
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of secondary hypogonadism. Some of these factors are related to the natural aging process, while others may be due to underlying medical conditions or lifestyle choices. In this section, we will discuss the most common causes and risk factors associated with secondary hypogonadism in older men.
As men age, the production of testosterone generally declines. This is a natural part of the aging process and is not necessarily a cause for concern. However, certain medical conditions can lead to secondary hypogonadism, including pituitary tumors, hypothalamic disorders, and certain genetic conditions. In addition, certain medications, such as opioids and steroids, can also contribute to the development of this condition. Lifestyle factors, such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise, can also increase the risk of developing secondary hypogonadism.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Secondary Hypogonadism
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of secondary hypogonadism, as they can have a significant impact on a man's quality of life. In this section, we will discuss the most common symptoms associated with this condition and how they can affect daily life.
Some of the most common symptoms of secondary hypogonadism include fatigue, low libido, erectile dysfunction, and mood changes. Men may also experience a decrease in muscle mass and strength, as well as an increase in body fat. These symptoms can lead to feelings of depression and a decreased sense of well-being, making it important to address and treat the underlying cause of secondary hypogonadism.
Diagnosing and Treating Secondary Hypogonadism
If you suspect that you may be experiencing secondary hypogonadism, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. In this section, we will discuss the diagnostic process for secondary hypogonadism and the various treatment options that may be available to you.
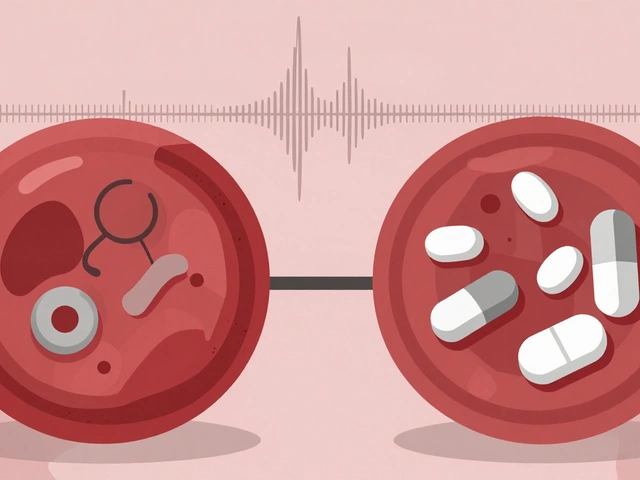
Diagnosing secondary hypogonadism typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to measure hormone levels. If the cause of the condition is determined to be related to the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, additional testing may be required to identify the specific issue. Treatment for secondary hypogonadism will depend on the underlying cause and may include hormone replacement therapy, medications, or lifestyle changes such as weight loss and exercise.
The Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy
One of the most common treatments for secondary hypogonadism is testosterone replacement therapy. This treatment aims to restore normal testosterone levels in the body, which can help alleviate many of the symptoms associated with the condition. In this section, we will discuss the potential benefits and risks of testosterone replacement therapy for men with secondary hypogonadism.
Testosterone replacement therapy can be administered in various forms, including injections, patches, gels, and pellets. The goal of this treatment is to improve symptoms such as fatigue, low libido, and erectile dysfunction, as well as increase muscle mass and bone density. However, testosterone replacement therapy is not without risks. Potential side effects include acne, sleep apnea, and an increased risk of blood clots. It is important to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider before beginning testosterone replacement therapy.
Addressing Lifestyle Factors
In addition to medical treatments, addressing lifestyle factors can also play a significant role in managing secondary hypogonadism. By making certain changes to your daily routine, you may be able to improve your symptoms and overall quality of life. In this section, we will discuss some of the lifestyle changes that can have a positive impact on men with secondary hypogonadism.
Some of the most effective lifestyle changes for addressing secondary hypogonadism include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and reducing stress levels. By focusing on these areas, you can help to naturally increase testosterone levels in the body and improve your overall health and well-being. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that addresses your specific needs and concerns.




Earl Hutchins May 4, 2023
Secondary hypogonadism often flies under the radar, but recognizing its signals can spark a health turnaround. The hypothalamus‑pituitary axis quietly orchestrates testosterone, so any hiccup calls for a check‑up. Lifestyle tweaks like shedding excess pounds and swapping sugary snacks for protein boost the natural hormone flow. If labs flag low testosterone, a thoughtful discussion about TRT versus lifestyle fixes is key. Keep the dialogue open with your doc; early action can preserve vigor.
Tony Bayard May 6, 2023
When the aging mind meets the whisper of a sluggish hypothalamus, the body erupts in a silent drama that many men overlook. The cascade from the pituitary to the testes is akin to a tightly choreographed ballet, and any misstep reverberates through energy, mood, and desire. Imagine waking each morning with a fog that clings to your thoughts like lingering smoke after a midnight fire. That fog is not merely fatigue; it is the echo of dwindling testosterone seeking a stage. Your muscles may betray you, losing the firm grip they once held, while adipose tissue fills the gaps with an unwelcome bravado. The psychological curtain rises, revealing irritability, a dimming libido, and a melancholy that feels like an endless winter. Yet, the plot thickens with medical culprits-opioid regimens, corticosteroid courses, and pituitary neoplasms-each a villain that can sabotage the hormonal script. Diagnosing this condition is a meticulous investigation: a thorough history, a physical exam, and the decisive blood draw that measures LH, FSH, and total testosterone. When the labs whisper low testosterone together with normal gonadotropins, the diagnosis of secondary hypogonadism stands illuminated. Treatment options unveil themselves like a toolbox: lifestyle reconstruction, addressing underlying pathologies, and the controversial but often effective testosterone replacement therapy. Lifestyle reconstruction-weight loss, resistance training, and macro‑balanced nutrition-can rekindle the body's own production, much like reigniting a dormant ember. When the root cause lies within the hypothalamus or pituitary, specific interventions such as pulsatile GnRH therapy may be warranted, a nuanced approach few clinicians master. TRT, whether delivered by gel, patch, injection, or pellet, promises a rapid rebound of vigor, but it carries a litany of potential side effects that must be weighed like scales in a courtroom. Acne flares, polycythemia, sleep apnea exacerbation, and a subtle increase in thrombotic risk are the shadows that follow the bright promise of restored testosterone. Thus, the saga of secondary hypogonadism demands a balanced perspective, an alliance between patient and physician, and a willingness to navigate both the scientific literature and the personal narrative toward reclaimed vitality.
Jay Crowley May 7, 2023
A concise lab panel will confirm the diagnosis.
sharon rider May 9, 2023
The interplay between endocrine signals and cultural expectations of masculinity often adds a silent burden to those experiencing secondary hypogonadism. While the physiological mechanisms are well‑documented, the personal narrative varies across societies, shaping how men perceive fatigue or loss of libido. Recognizing that mood changes may stem from both hormonal shifts and societal pressures can guide a more compassionate therapeutic approach. Engaging in reflective conversations with healthcare providers about these layered experiences fosters trust. Ultimately, integrating physiological treatment with cultural awareness may improve outcomes beyond mere symptom control.
swapnil gedam May 11, 2023
Many men discount subtle signs like reduced stamina or a gradual dip in confidence, attributing them to "just getting older." Yet, research shows that secondary hypogonadism can be precipitated by factors we control, such as chronic opioid use or unmanaged obesity. A balanced diet rich in zinc and vitamin D, combined with regular resistance training, can naturally stimulate the hypothalamic‑pituitary axis. Moreover, reviewing medication lists with a clinician may uncover iatrogenic contributors that are reversible. If lifestyle adjustments fall short, a targeted hormone panel can clarify whether TRT is warranted. Open communication with a trusted physician ensures that treatment decisions align with personal health goals and risk tolerance. Remember, proactive steps today can stave off the cascade of metabolic complications tomorrow.
Michael Vincenzi May 12, 2023
Great points! I’ve seen patients bounce back dramatically after swapping sedentary habits for short daily walks and a protein‑focused breakfast. It’s also reassuring to know that doctors can adjust meds to reduce hormonal interference. If someone feels stuck, encouraging a candid chat with their provider can open doors to tailored solutions.
Courage Nguluvhe May 13, 2023
From a clinical standpoint, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a double‑edged sword; its pharmacokinetics demand rigorous monitoring. Intramuscular esters provide stable serum peaks but can cause supraphysiologic spikes, while transdermal gels offer smoother curves yet risk dermal transfer. The risk‑benefit calculus must factor in hematocrit elevation, lipid profile perturbations, and potential prostate-specific antigen (PSA) fluctuations. Practitioners should implement a structured protocol: baseline labs, 3‑month follow‑up, and periodic cardiovascular assessments. In settings where comorbidities exist, alternative strategies like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) may be more prudent. Ultimately, evidence‑based dosing and vigilant surveillance are non‑negotiable to mitigate iatrogenic complications.