Anticoagulants: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
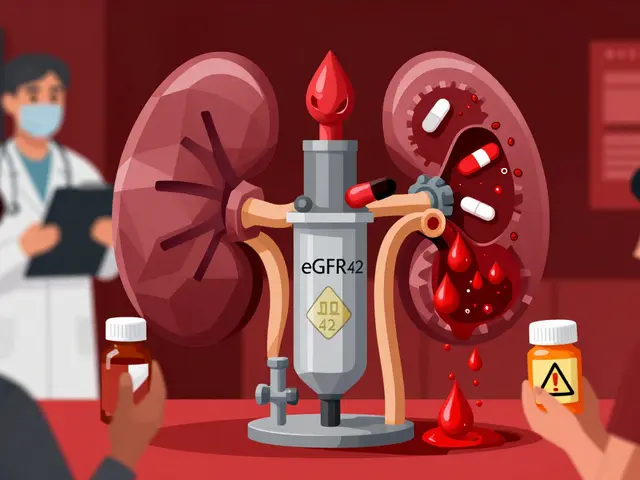
When your blood starts clotting where it shouldn’t — inside your heart, lungs, or legs — anticoagulants, medications that slow down the blood’s ability to form clots. Also known as blood thinners, they don’t actually thin your blood. They interrupt the clotting process to keep dangerous clots from forming or growing. This isn’t just about preventing strokes or heart attacks. For people with atrial fibrillation, artificial heart valves, or a history of deep vein thrombosis, anticoagulants can be life-saving.
Not all anticoagulants work the same way. Some, like warfarin, a long-used oral anticoagulant that affects vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, need regular blood tests to make sure the dose is right. Others, like heparin, a fast-acting injectable anticoagulant often used in hospitals, kick in quickly but don’t last long. Then there are newer options like apixaban and rivaroxaban — simpler to use, fewer food interactions, no routine monitoring. But they’re not for everyone. Your kidney function, age, other meds, and even your diet can change which one is safest for you.
Anticoagulants don’t come without risks. Bleeding is the big one — a cut that won’t stop, unusual bruising, or even internal bleeding you don’t see. That’s why knowing the warning signs matters. If you’re on one of these drugs, you need to know when to call your doctor. Some people switch from brand-name to generic versions and notice changes — nausea, dizziness, or worse. That’s not normal. It’s not just about the drug name. It’s about how your body reacts.
You’ll also find posts here that connect anticoagulants to other conditions. For example, someone with cancer might need anticoagulants because tumors increase clot risk. Or a person on dialysis might be on one to keep their access site clear. Even when you’re taking these meds for heart issues, other drugs you’re on — like antibiotics or pain relievers — can interfere. That’s why understanding the full picture matters.
There’s no one-size-fits-all anticoagulant. What works for your neighbor might not work for you. That’s why the guides below cover real cases: how people manage side effects, what alternatives exist, and when to push back if something feels off. Whether you’re just starting out or have been on one for years, these posts give you the practical, no-fluff info you need to stay safe and in control.
Anticoagulants in Seniors: Fall Risk vs. Stroke Prevention
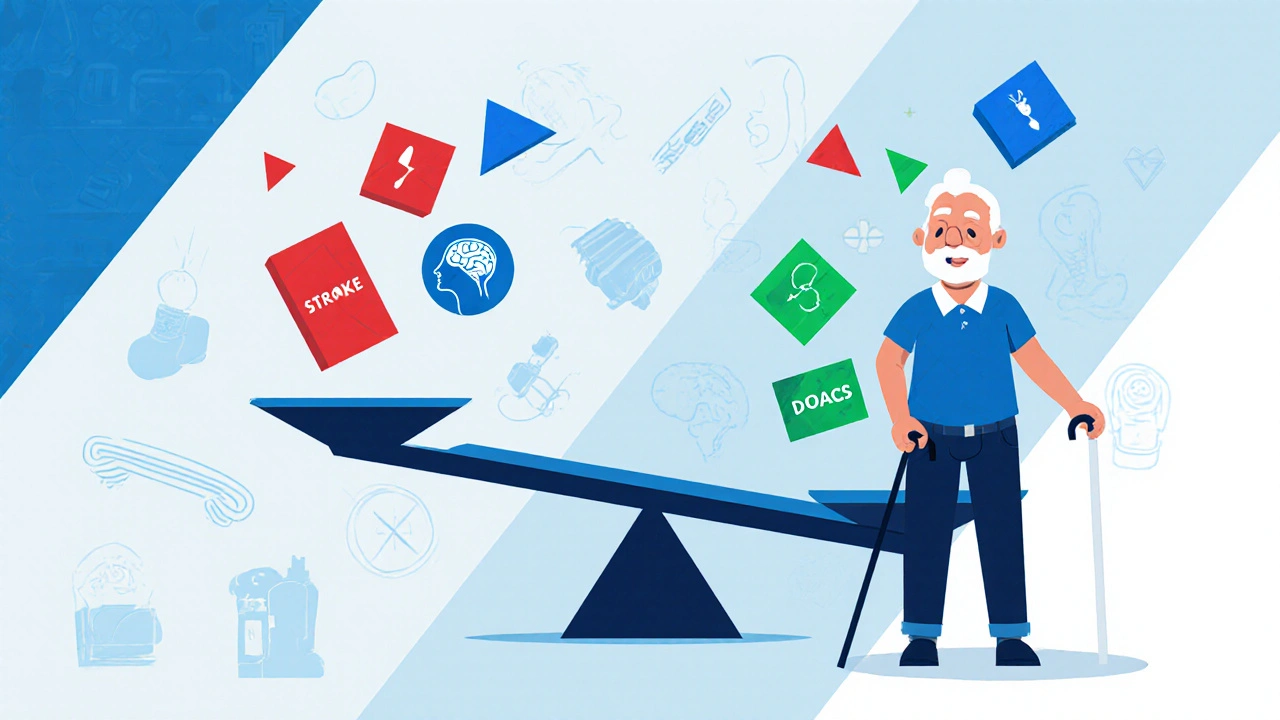
Anticoagulants prevent strokes in seniors with atrial fibrillation-even with fall risk. Evidence shows the benefits far outweigh the dangers, and DOACs like apixaban offer safer, easier options than warfarin.
Head Injury While on Blood Thinners: When to Get Imaging
If you're on blood thinners and hit your head, even a minor injury can lead to dangerous brain bleeding. Learn when to get a CT scan, what to watch for after a normal result, and why waiting can be life-threatening.
Anticoagulants and Bleeding Disorders: How to Prevent Hemorrhage Safely
Learn how to prevent dangerous bleeding while taking anticoagulants. Understand risks, drug differences, reversal agents, and practical steps to stay safe on blood thinners like warfarin and DOACs.
Falls Risk on Anticoagulants: How to Prevent Bleeding and Stay Safe
Falls don’t mean you should stop blood thinners. Learn why DOACs are safer for fall-risk patients, how to prevent falls without quitting medication, and when anticoagulation is truly necessary for stroke prevention.